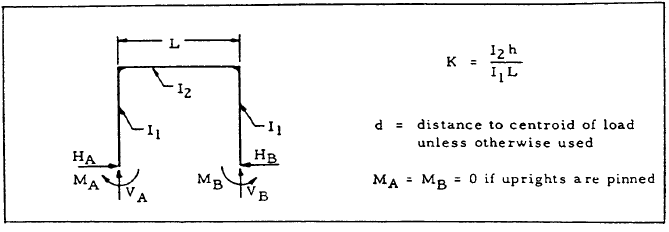
Formulas for Simple Frames
This section presents formulas for determining the reaction forces and moments acting on simple frames under various simple loadings. The reaction forces and moments acting on frames under more complicated loadings may often be obtained by the superposition of these simple loadings.
- Frames and Rings
- Formulas for Simple Frames
- Circular Rings & Arches
The content of this page is taken from the "Stress Analysis Manual," Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory, October 1986. Other related chapters from the Air Force "Stress Analysis Manual" can be seen above.
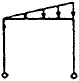
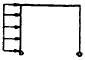
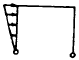
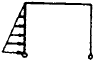
Cases 1 through 9 of Table 5-3 give reaction forces and moments on rectangular frames, both of whose uprights are pinned; and such frames with both uprights fixed are treated by cases 9 through 18 of this table. Table 5-4 gives reaction forces and moments on trapezoidal frames. The first four cases treat such frames with both uprights pinned at the ends, and cases 5 and 6 treat trapezoidal frames with fixed- ended uprights. Table 5-5 gives reaction forces and moments on triangular frames.
Table 5-3
Reaction Forces and Moments on Rectangular Frames
| Case | Frame | Forces & Moments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
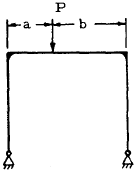
| 1 |
|
For Special Case: \( a = b = L/2 \)
|
|||||
| 2 |
|
For Special Case: \( a = c = 0 \), \( b = L \)
|
|||||
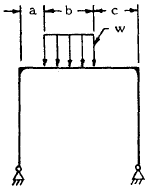
| 3 |
|
For Special Case: \( a = 0 \), \( b = L \), \( d = { L \over 3 } \)
|
|||||
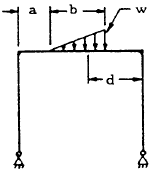
| 4 |
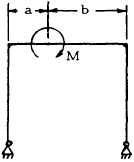
|
$$ V_A = -V_B = { -M \over L } $$
$$ H_A = H_B = { 3 (b - L/2) M \over Lh (2K + 3) } $$
|
|||||
| 5 |
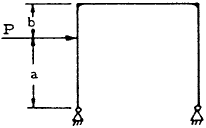
|
$$ V_A = -V_B = { -Pa \over L } $$
$$ H_B = { Pa \over 2h } \left[ { bK(a+h) \over h^2 (2K+3) } + 1 \right] $$
$$ H_A = H_B - P $$
|
|||||
| 6 |
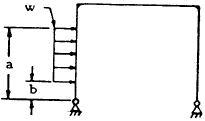
|
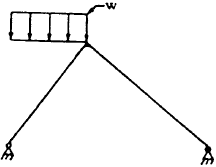
$$ V_A = -V_B = { w(b^2 - a^2) \over 2L } $$
$$ H_B = { w (a^2 - b^2) \over 4h } + { K [ w (a^2 - b^2) (2h^2 - a^2 - b^2) ] \over 8 h^3 (2K + 3) } $$
$$ H_A = H_B + w(b-a) $$
For Special Case: \( b = 0 \), \( a = h \)
$$ H_B = { wh \over 4 } \left[ 1 + { K \over 2 (2K + 3) } \right] $$
$$ H_A = H_B - wh $$
|
|||||
| 7 |
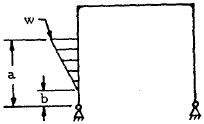
|
$$ V_A = -V_B = {w \over 6L} (2a + b) (b-a) $$
$$ H_B = { -V_A L \over 2h } + { K X_{10} \over h (2K + 3) } $$
where:
$$
\begin{eqnarray}
X_{10} &=& { w \over 120 h^2 (a-b) } ~[-30 h^2 b (a^2 - b^2) \nonumber \\
&+& 20 h^2 (a^2 - b^2) + 15 b (a^4 - b^4) - 12 (a^5 - b^5)]
\end{eqnarray}
$$
$$ H_A = H_B + { w (b-a) \over 2 } $$
For Special Case: \( b = 0 \), \( a = L \)
$$ H_B = { wh \over 10 } \left({ 4K+5 \over 2K + 3 }\right) $$
$$ H_A = H_B - {wh \over 2} $$
|
|||||
| 8 |
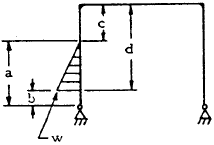
|
$$ V_A = -V_B = {-w \over 6L} (a^2 + ac - 2c^2) $$
$$ H_B = { -V_A L \over 2h } + { K X_7 \over (2K + 3)h } $$
where:
$$
\begin{eqnarray}
X_7 &=& { w \over 120 h^2 (d-c) } ~[3 (4d^5 + c^5) - 15h (3d^4 + c^4) \nonumber \\
&+& 20 h^2 (2d^3 + c^3) - 15cd^2 (2h-d)^2 ]
\end{eqnarray}
$$
For Special Case: \( b = c = 0 \), \( a = d = h \)
$$ H_B = { wh \over 12 } \left[ 1 + { 7K \over 10(2K + 3) } \right] $$
|
|||||
| 9 |
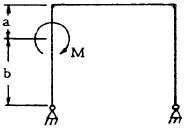
|
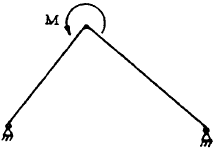
$$ V_A = -V_B = { -M \over L } $$
$$ H_A = H_B = { 3 [ K(2ab + a^2) + h^2 ] M \over 2h^3 (2K + 3) } $$
|
|||||
| 10 |
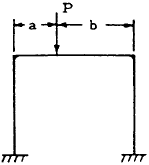
|
$$ H_A = H_B = { 3Pab \over 2Lh(K+2) } $$
$$ M_A = {Pab \over L} \left[ {1 \over 2(K+2)} - { (b-a) \over 2L(6K+1)) } \right] $$
$$ M_B = {Pab \over L} \left[ {1 \over 2(K+2)} + { (b-a) \over 2L(6K+1)) } \right] $$
For Special Case: \( a = b = L/2 \)
$$ H_A = H_B = { 3PL \over 8h(K+2) } $$
$$ M_A = M_B = { PL \over 8(K+2) } $$
|
|||||
| 11 |
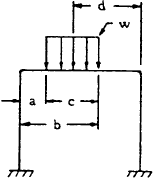
|
$$ H_A = H_B = { 3 (X_1 + X_2) \over 2h(K+2) } $$
$$ M_A = { X_1 + X_2 \over 2(K+2) } - { X_1 - X_2 \over 2(6K + 1) } $$
$$ M_B = { X_1 + X_2 \over 2(K+2) } + { X_1 - X_2 \over 2(6K + 1) } $$
where:
$$ X_1 = {-wc \over 24L} \left[ {24d^3 \over L} - {6bc^2 \over L} + {3c^2 \over L} + 4c^2 - 24d^2 \right] $$
$$ X_2 = {wc \over 24L} \left[ {24d^3 \over L} - {6bc^2 \over L} + {3c^2 \over L} + 2c^2 - 48d^2 + 24dL \right] $$
For Special Case: \( a = 0 \), \( c = b = L \), \( d = L/2 \)
$$ H_A = H_B = { wL^2 \over 4h(K+2) } $$
$$ M_A = M_B = { wL^2 \over 12(K+2) } $$
|
|||||
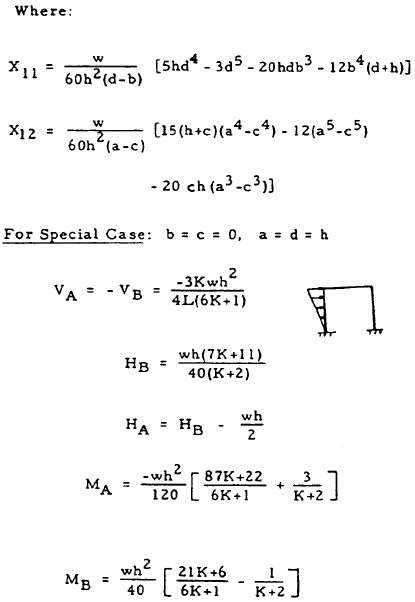
| 12 |
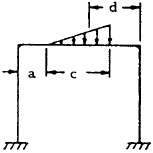
|
$$ H_A = H_B = { 3 (X_3 + X_4) \over 2h(K+2) } $$
$$ M_A = { X_3 + X_4 \over 2(K+2) } - { X_3 - X_4 \over 2(6K + 1) } $$
$$ M_B = { X_3 + X_4 \over 2(K+2) } + { X_3 - X_4 \over 2(6K + 1) } $$
where:
$$ X_3 = {-wc \over 2L} \left[ {d^3 \over L} + {c^2 \over 9} + {51c^3 \over 810L} + {c^2b \over 6L} - d^2 \right] $$
$$ X_4 = {wc \over 2L} \left[ {d^3 \over L} + {c^2 \over 18} + {51c^3 \over 810L} - {c^2b \over 6L} - 2d^2 + dL \right] $$
For Special Case: \( a = 0 \), \( c = b = L \), \( d = L/3 \)
$$ H_A = H_B = { wL^2 \over 8h(K+2) } $$
$$ M_A = { wL^2 \over 120 } \left( {5 \over K+2} + {1 \over 6K+1} \right) $$
$$ M_B = { wL^2 \over 120 } \left( {5 \over K+2} - {1 \over 6K+1} \right) $$
|
|||||
| 13 |
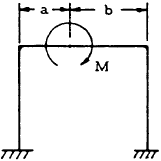
|
$$ V_A = -V_B = { -6 (ab + L^2 K) M \over L^3 (6K + 1) } $$
$$ H_A = H_B = { 3 (b-a) M \over 2Lh (K+2) } $$
$$ M_A = M \left\{ { 6ab(K+2) - L[ a(7K+3) - b(5K-1) ] \over 2L^2 (K+2) (6K+1) } \right\} $$
$$ M_B = M + M_A + V_A L $$
|
|||||
| 14 |
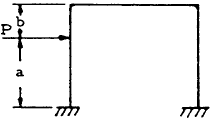
|
$$ V_A = -V_B = { -3 P a^2 K \over Lh(6K+1) } $$
$$ H_B = {Pa \over 2h} \left[ {h \over b} - { h + b + K(b-a) \over h(K+2) } \right] $$
$$ H_A = H_B - P $$
$$ M_A = {Pa \over 2h} \left[ {-b (h + b + bK) \over b(K+2)} - h + {3aK \over 6(K+1)} \right] $$
$$ M_B = {Pa \over 2h} \left[ {-b (h + b + bK) \over b(K+2)} + h - {3aK \over 6(K+1)} \right] $$
|
|||||
| 15 |
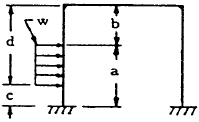
|

|
|||||
| 16 |
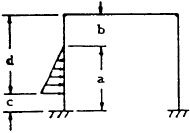
|
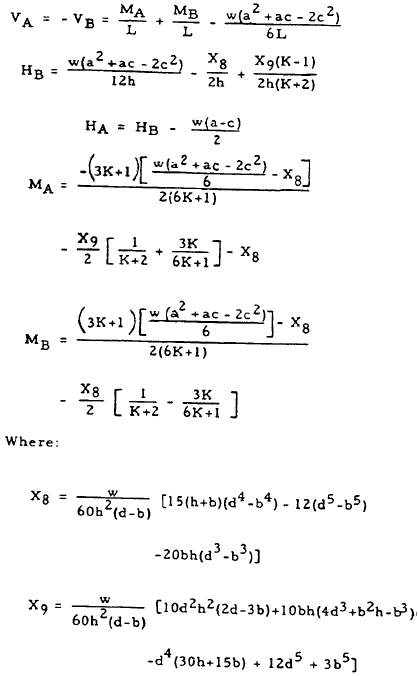
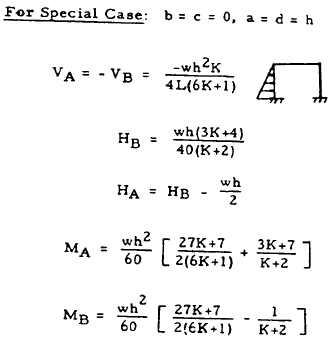
|
|||||
| 17 |
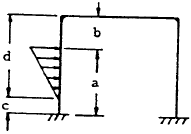
|
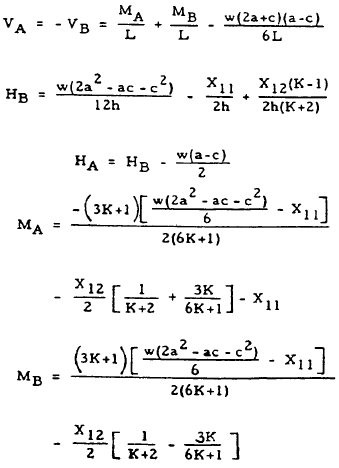
|
|||||
| 18 |
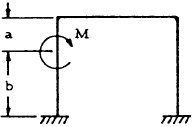
|
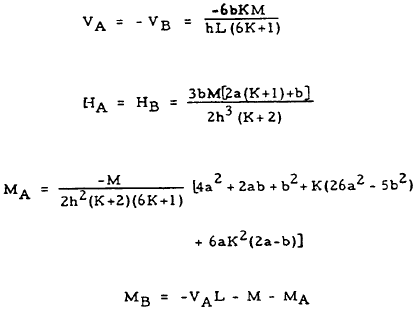
|
We have a number of structural calculators to choose from. Here are just a few:
Table 5-4
Rectangular Forces and Moments on Trapezoidal Frames
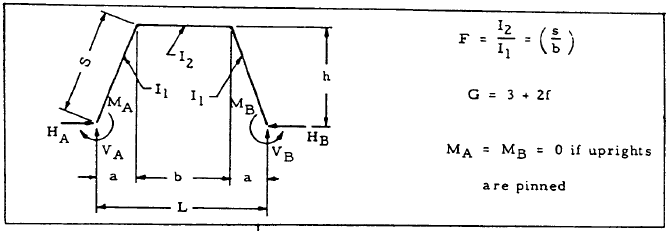
| Case | Frame | Forces & Moments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
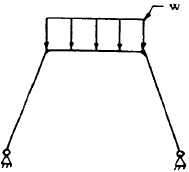
|
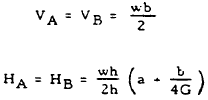
|
| 2 |
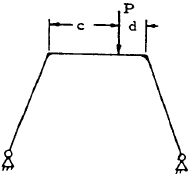
|
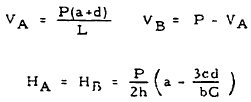
|
| 3 |
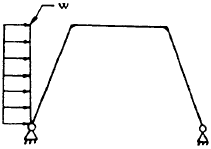
|
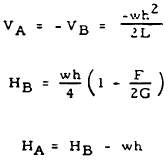
|
| 4 |
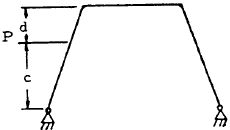
|
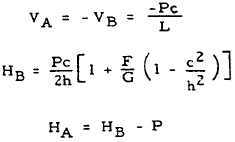
|
| 5 |
|
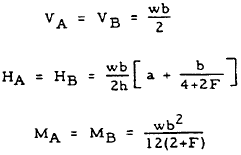
|
| 6 |
|
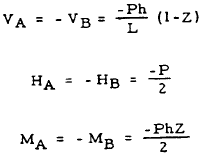
|
We have a number of structural calculators to choose from. Here are just a few:
Table 5-5
Rectangular Forces and Moments on Triangular Frames
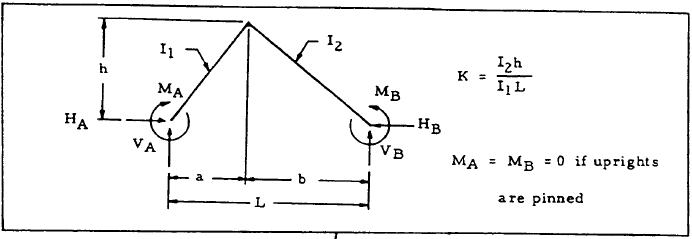
| Case | Frame | Forces & Moments |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |
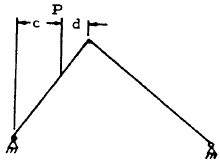
|
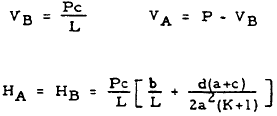
|
| 2 |
|
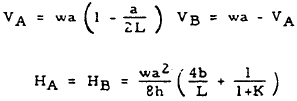
|
| 3 |
|
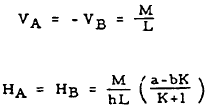
|
| 4 |
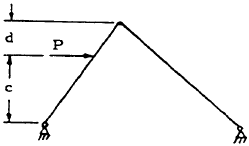
|
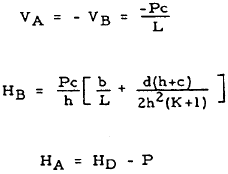
|
| 5 |
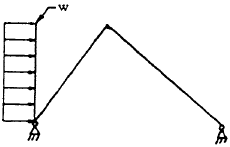
|
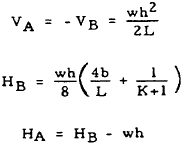
|
| 6 |
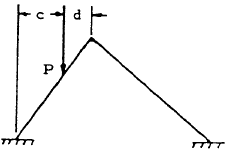
|
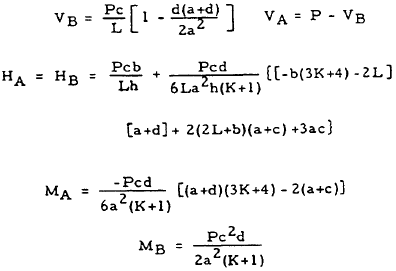
|
| 7 |
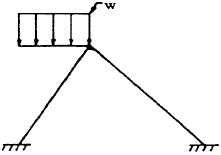
|
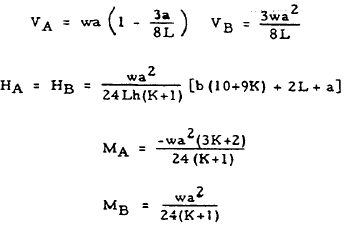
|
| 8 |
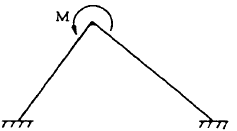
|
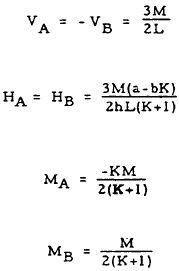
|
| 9 |
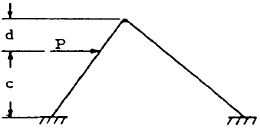
|
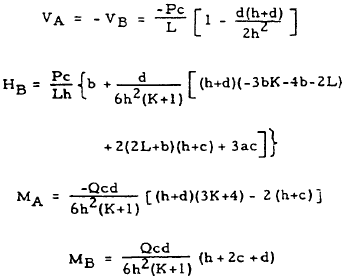
|
| 10 |
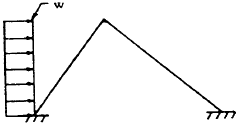
|
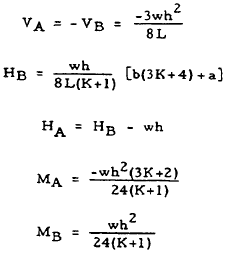
|
We have a number of structural calculators to choose from. Here are just a few:
5.8 Sample Problem - Formulas for Simple Frames
Given: The trapezoidal frame shown in Figure 5-14.
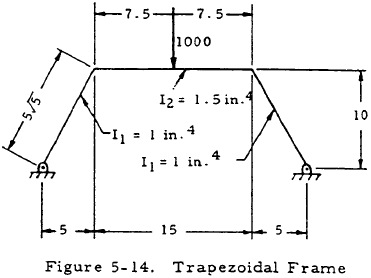
Find: The reaction forces and bending moments.
Solution: From the diagram at the top of Table 5-4,
$$ F = { I_2 \over I_1 } \left({s \over b}\right) = { 1.5 \over 1 } \left({5 \sqrt{5} \over 15}\right) = 1.12 $$ $$ G = 3 + 2F = 3 + 2(1.12) = 5.24 $$From Table 5-4, case 2,
$$ V_A = { P(a + d) \over L } = { 1000 (5 + 7.5) \over 25 } = 500 ~\text{lb.} $$ $$ V_B = P - V_A = 1000 - 500 = 500 ~\text{lb.} $$ $$ H_A = H_B = { P \over 2h } \left( a + { 3 c d \over b G } \right) = { 1000 \over 2(10) } \left[ 5 + { 3(7.5)(7.5) \over 15(5.24) } \right] = 357 ~\text{lb.} $$A free-body diagram may be constructed for a section of the frame leg, as shown in Figure 5-15. Equating the sum of the moment to zero gives
$$ M = -500 x_1 + 357 (2 x_1) = 214 x_1 $$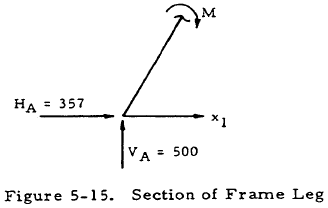
At the left frame joint,
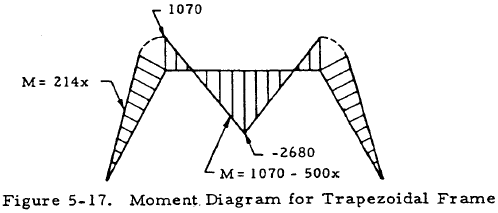
$$ M = 214x = 214(5) = 1070 ~\text{in.lb.} $$A free-body diagram may now be drawn for a section of the horizontal portion of the frame to the left of the load as in Figure 5-16. Equating the sum of the moments to zero gives
$$ M = 1070 - 500 x_2 $$By considering symmetry, the moment diagram of the given frame may be drawn as shown in Figure 5-17.